 Zerodha (Trading Account)
Zerodha (Trading Account)
FREE Equity Delivery and MF
Flat ₹20/trade Intra-day/F&O
 Zerodha (Trading Account)
Zerodha (Trading Account)
FREE Equity Delivery and MF
Flat ₹20/trade Intra-day/F&O

|
|
Compare Protective Call (Synthetic Long Put) and Box Spread (Arbitrage) options trading strategies. Find similarities and differences between Protective Call (Synthetic Long Put) and Box Spread (Arbitrage) strategies. Find the best options trading strategy for your trading needs.
| Protective Call (Synthetic Long Put) | Box Spread (Arbitrage) | |
|---|---|---|
 |
 |
|
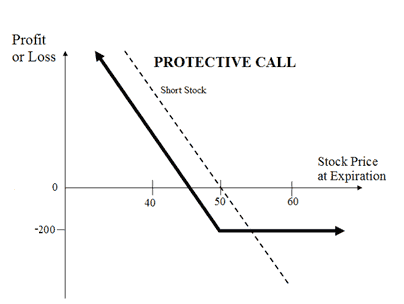
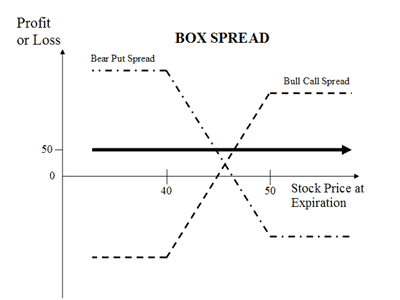
| About Strategy | The Protective Call strategy is a hedging strategy. In this strategy, a trader shorts position in the underlying asset (sell shares or sell futures) and buys an ATM Call Option to cover against the rise in the price of the underlying. This strategy is opposite of the Synthetic Call strategy. It is used when the trader is bearish on the underlying asset and would like to protect 'rise in the price' of the underlying asset. The risk is limited in the strategy while the rewards are unlimited. How to use a Protective Call trading strategy? The usual Protective Call Strategy looks like as below for State Bank of India (SBI) Shares which are currently traded at Rs 275 (SBI Spot Price): Protective Call Orders - SBI Stock Orde... Read More | Box Spread (also known as Long Box) is an arbitrage strategy. It involves buying a Bull Call Spread (1 ITM and I OTM Call) together with the corresponding Bear Put Spread (1 ITM and 1 OTM Put), with both spreads having the same strike prices and expiration dates. The strategy is called Box Spread as it is combination of 2 spreads (4 trades) and the profit/loss calculated together as 1 trade. Note that the total cost of the box remain same irrespective to the price movement of underlying security in any direction. The expiration value of the box spread is actually the difference between the strike prices of the options involved. The Long Box strategy is opposite to Short Box strategy. It is used when the spreads are under-priced with respe... Read More |
| Market View | Bearish | Neutral |
| Strategy Level | Beginners | Advance |
| Options Type | Call + Underlying | Call + Put |
| Number of Positions | 2 | 4 |
| Risk Profile | Limited | None |
| Reward Profile | Unlimited | Limited |
| Breakeven Point | Underlying Price - Call Premium | |
| Protective Call (Synthetic Long Put) | Box Spread (Arbitrage) | |
|---|---|---|
| When to use? | The Protective Call option strategy is used when you are bearish in market view and want to short shares to benefit from it. The strategy minimizes your risk in the event of prime movements going against your expectations. |
Being risks free arbitrage strategy, this strategy can earn better return than earnings in interest from fixed deposits. The earning from this strategy varies with the strike price chosen by the trader. i.e. Earning from strike price '10400, 10700' will be different from strike price combination of '9800,11000'. The long box strategy should be used when the component spreads are underpriced in relation to their expiration values. In most cases, the trader has to hold the position till expiry to gain the benefits of the price difference. Note: If the spreads are overprices, another strategy named Short Box can be used for a profit. This strategy should be used by advanced traders as the gains are minimal. The brokerage payable when implementing this strategy can take away all the profits. This strategy should only be implemented when the fees paid are lower than the expected profit. |
| Market View | Bearish When you are bearish on the underlying but want to protect the upside. |
Neutral The market view for this strategy is neutral. The movement in underlying security doesn't affect the outcome (profit/loss). This arbitrage strategy is to earn small profits irrespective of the market movements in any direction. |
| Action |
|
Say for XYZ stock, the component spreads are underpriced in relation to their expiration values. The trader could execute Long Box strategy by buying 1 ITM Call and 1 ITM Put while selling 1 OTM Call and 1 OTM Put. There is no risk of loss while the profit potential would be the difference between two strike prices minus net premium. |
| Breakeven Point | Underlying Price - Call Premium When the price of the underlying is equal to the total of the sale price of the underlying and premium paid. |
| Protective Call (Synthetic Long Put) | Box Spread (Arbitrage) | |
|---|---|---|
| Risks | Limited The maximum loss is limited to the premium paid for buying the Call option. It occurs when the price of the underlying is less than the strike price of Call Option. Maximum Loss = Call Strike Price - Sale Price of Underlying + Premium Paid |
None The Box Spread Options Strategy is a relatively risk-free strategy. There is no risk in the overall position because the losses in one spread will be neutralized by the gains in the other spread. The trades are also risk-free as they are executed on an exchange and therefore cleared and guaranteed by the exchange. The small risks of this strategy include:
|
| Rewards | Unlimited The maximum profit is unlimited in this strategy. The profit is dependent on the sale price of the underlying. Profit = Sale Price of Underlying - Price of Underlying - Premium Paid |
Limited The reward in this strategy is the difference between the total cost of the box spread and its expiration value. Being an arbitrage strategy, the profits are very small. It's an extremely low-risk options trading strategy. |
| Maximum Profit Scenario | Underlying goes down and Option not exercised |
|
| Maximum Loss Scenario | Underlying goes down and Option exercised |
| Protective Call (Synthetic Long Put) | Box Spread (Arbitrage) | |
|---|---|---|
| Advantages | Minimizes the risk when entering into a short position while keeping the profit potential limited. |
|
| Disadvantage | Premium paid for Call Option may eat into your profits. |
|
| Simillar Strategies | Long Put |

Add a public comment...

FREE Intraday Trading (Eq, F&O)
Flat ₹20 Per Trade in F&O
|
|